| ME5332 FINAL EXAMINATION |
| 02:00-03:30PM, May 7, 2021 |
- Find the fluid velocity components (u,v) for a complex potential function given as
f(z) = z + i z. - Approximate ex by d1 + d2 x over [0, 1] using the least square method.
-
Obtain the first two ON functions, (e1, e2), over [0, 2] by the Gram-Schmidt procedure for
a1 = 1 and a2 = x where the inner product is defined as
(f, g) = ⌠
⌡2
0x f(x) g(x) dx. - Using (e1, e2) in Problem 3, expand f(x)=x3 by a linear combination of e1 and e2 over [0, 2].
-
Find the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions for
L en = λn en, L ≡ − d2 dx2, en′(−1) = en(0)=0. -
Solve
using the eigenfunction expansion method and write down the first two terms.−u"(x)=x, u′(−1)=u(0)=0, -
Find a one-term approximate solution to the differential equation,
(u"+x u=1) using the Galerkin method. Choose a base function which vanishes at x = 0, 1.L u = 1, L ≡ d2 dx2+x, u(0) = u(1) = 0, -
Using the Neumann series approach, compute A−1 where
A ≡ ⎛
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝1 −1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 ⎞
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠. -
Solve the Laplace equation,
∂2 u ∂x2+ ∂2 u ∂y2= 0,
with the boundary condition shown by the eigenfunction expansion method.{(x,y),0 ≤ x ≤ 1, −∞ < y ≤ 0 } 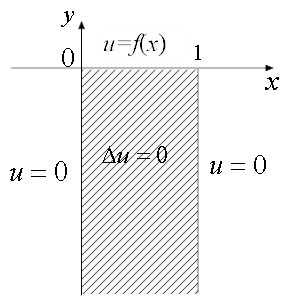
- Rewrite
in a weak form.−u"(x)+ ex u(x) = x, u(0)=u(1)=0,
| Solution |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 7.
Choose e(x) = x (1−x). Then e′(x) = 1 − 2 x and e"(x) = −2.
7.
Choose e(x) = x (1−x). Then e′(x) = 1 − 2 x and e"(x) = −2.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|