 Pink noise
Pink noise 
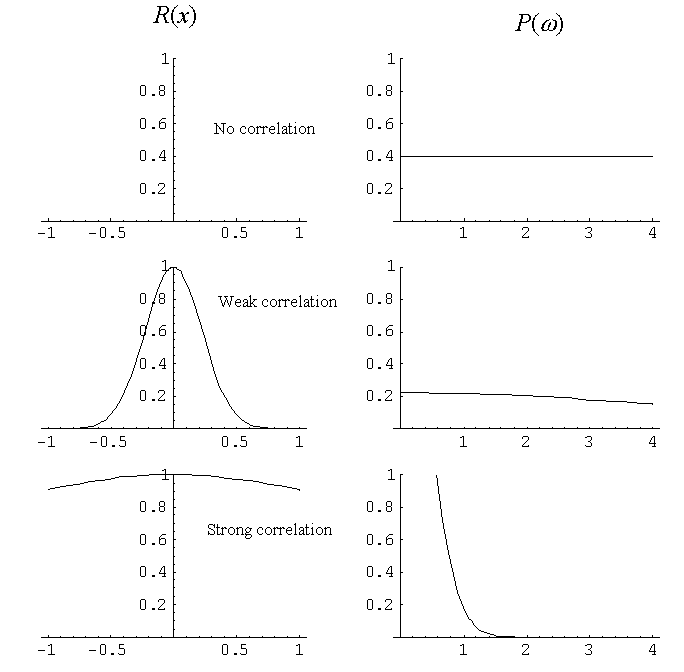 If P(ω) is independent of the frequency, it is called white noise.
If P(ω) is proportional to 1/f ( = 1/ω), the original data is called pink noise,
1/f noise or fractal noise and if P(ω) is proportional to 1/f2, it is called
brown noise.
If P(ω) is independent of the frequency, it is called white noise.
If P(ω) is proportional to 1/f ( = 1/ω), the original data is called pink noise,
1/f noise or fractal noise and if P(ω) is proportional to 1/f2, it is called
brown noise.
 White noise
White noise 
| (1) |
| (2) |
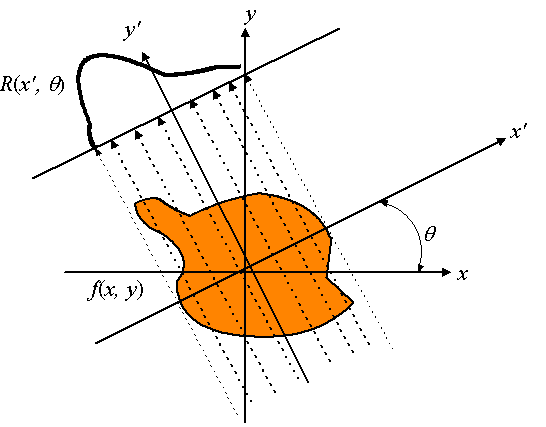 Note that R(x′, θ) depends on x′ and θ.
The Fourier transform for a two variable function, f(x, y), is defined as
Note that R(x′, θ) depends on x′ and θ.
The Fourier transform for a two variable function, f(x, y), is defined as
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
|
| (11) |