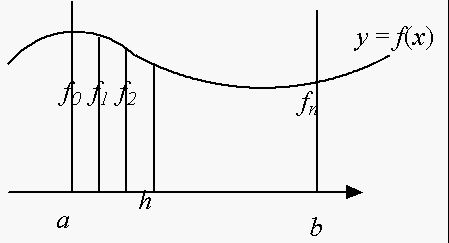
|
|
- C code
Online C compiler Online C compiler(alternative)/* Rectangular rule */ #include <stdio.h> double f(double x) {return 4.0/(1.0+x*x) ; } int main() { int i, n; double a=0.0, b=1.0, h, s=0.0 , x ; /* printf("Number of partitions = "); scanf("%d", &n) ; */ n=10; h = (b-a)/n ; for (i= 0;i<n;i++) s = s + f(a + i*h) ; s=s*h ; printf("Result =%20.12f\n", s) ; return 0; }
- MATLAB (Octave) code
Online Octave (Matlab)f = @(x) 4/(1+x^2); a=0;b=1;s=0; n=10; %n=input('Enter n='); h=(b-a)/n; for i=0:1:n-1 s=s+f(a+i*h); end; s=s*h; fprintf('%f\n', s);

|
|
- C code
Online C compiler Online C compiler(alternative)/* Trapezoidal rule */ #include <stdio.h> double f(double x) {return 4.0/(1.0+x*x);} int main() { int i, n ; double a=0.0, b=1.0 , h, s=0.0, x; /* printf("Enter number of partitions = "); scanf("%d", &n) ; */ n=10; h = (b-a)/n ; for (i=1;i<=n-1;i++) s = s + f(a + i*h); s=h/2*(f(a)+f(b))+ h* s; printf("%20.12f\n", s) ; return 0; } - MATLAB (Octave) code
Online Octave (Matlab)f = @(x) 4/(1+x^2); a=0;b=1;s=0; n=10; %n=input('Enter n='); h=(b-a)/n; for i=1:1:n-1 s=s+f(a+i*h); end; s=h/2*(f(a)+f(b))+h*s; fprintf('%f\n', s);
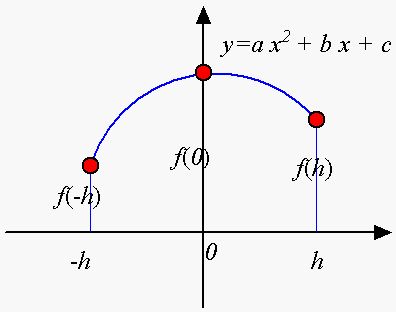 Approximate the curve that passes (−h, f(−h)), (0, f(0)) and (h, f(h)) by
Approximate the curve that passes (−h, f(−h)), (0, f(0)) and (h, f(h)) by
| (3) |
|
|
|
| (11) |
|