
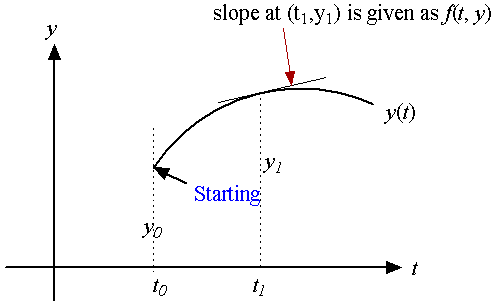
| (1) |
| (2) |

|
| (3) |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
double f(double t, double y)
{
return y;
}
int main()
{
double h = 0.1, t, y, k1, k2, k3, k4;
int i;
/* initial value */
t = 0.0; y = 1.0;
for (i = 0; i<=10; i++)
{
printf("t= %f rk= %f exact=%f\n", t, y, exp(t));
k1 = h * f(t,y);
k2 = h * f(t + h/2, y + k1/2.0);
k3 = h * f(t + h/2, y + k2/2.0);
k4 = h * f(t + h, y + k3);
y = y + (k1 + 2.0 * k2 + 2.0 * k3 + k4)/6.0;
t = t + h;
}
return 0;
}
|
| (4) |
|
|
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
double f1(double t, double y1, double y2)
{
return y2;
}
double f2(double t, double y1, double y2)
{
return -y1;
}
int main()
{
double h = 0.02, y1, y2, t;
int i;
y1 = 0.0; y2 = 1.0;
t = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i<=100; i++)
{
printf("%f %f %f\n", t, y1, sin(t));
y1 = y1 + h * f1(t, y1, y2);
y2 = y2 + h * f2(t, y1, y2);
t = t + h;
}
return 0;
}
|
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define P 16.0
#define b 4.0
#define R 35.0
double f1(double u, double v, double w)
{
return P*(v-u);
}
double f2(double u, double v, double w)
{
return -u*w+R*u-v;
}
double f3(double u, double v, double w)
{
return u*v-b*w;
}
int main()
{
double h, t, u, v, w;
int i;
/* initial value */
t = 0.0; h = 0.01;
u = 5.0; v = 5.0; w = 5.0;
for (i = 0; i< 3000; i++)
{
u = u + h * f1(u,v,w);
v = v + h * f2(u,v,w);
w = w + h * f3(u,v,w);
printf("%f %f\n", u, w);
t = t + h;
}
return 0;
}
|
c:\tmp\gcc -o lorenz.exe lorenz.c c:\tmp\lorenz.exe > lorenz.dat (Launch gnuplot) Change directory to c:\tmp plot "lorenz.dat" with line |
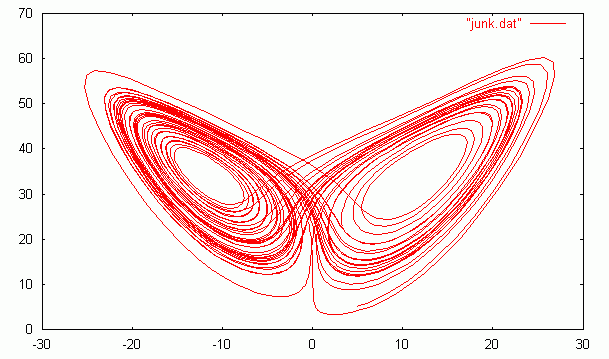 Here is a code in Matlab/Octave.
Here is a code in Matlab/Octave.
P=16;b=4;R=35; f1=@(u,v,w) P*(v-u); f2=@(u,v,w) -u*w+R*u-v; f3=@(u,v,w) u*v-b*w; t=0;h=0.01; u=5;v=5;w=5; for i=1:1:3000 u=u+h*f1(u,v,w); v=v+h*f2(u,v,w); w=w+h*f3(u,v,w); uu(i)=u;vv(i)=v; t=t+h; end; plot(uu',vv'); |
|
f=@(t,y) -t*t*y; tspan=linspace(0,5,100); y0=1; [t,y]=ode45(f, tspan, y0); plot(t,y); |
|
f=@(y,t) -t*t*y; tspan=linspace(0, 3, 100); y0=1; sol=lsode(f, y0, tspan); plot(tspan, sol); |


