#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
float power(float x, float y)
{
return exp(y*log(x));
}
int main()
{
float x,y;
printf("Enter x and y separated by space =");
scanf("%f %f",&x,&y);
if (x<0)
{
printf("x must be positive !!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("%f to power of exponent %f is %f.\n", x, y, power(x,y));
return 0;
}
|
#include <stdio.h>
float f(int n)
{
int i; float sum=0;
for (i=1;i < n;i++) sum=sum+1.0/i;
return sum;
}
int main()
{
float sum=0;
int i;
for (i=1;i < 20;i++) sum=sum+1.0/i/i;
printf("%f %f\n", sum, f(20));
return 0;
}
|
#include <stdio.h>
int i=20;
void f()
{
printf("%d\n",i);
}
int main()
{
int i=30;
printf("%d\n", i);
f();
return 0;
}
|
- Fibonacci numbers

from Da Vinci Code. The Fibonacci numbers are defined as
This is related to the problem of how fast rabbits could breed in ideal circumstances studied by Fibonacci (Click this link).an = an−1+ an−2, a1 = 1, a2 = 1.  Suppose a newly-born pair of rabbits, one male, one female, are put in a field.
Rabbits are able to mate at the age of one month so that at the end of its second month a female can produce another pair of rabbits. Suppose that our rabbits never die and that the female always produces one new pair (one male, one female) every month from the second month on. The puzzle that Fibonacci posed was...
How many pairs will there be in two years (a24 = ?) ?
Code:
Suppose a newly-born pair of rabbits, one male, one female, are put in a field.
Rabbits are able to mate at the age of one month so that at the end of its second month a female can produce another pair of rabbits. Suppose that our rabbits never die and that the female always produces one new pair (one male, one female) every month from the second month on. The puzzle that Fibonacci posed was...
How many pairs will there be in two years (a24 = ?) ?
Code:
The explicit form of the Fibonacci sequence is given by#include <stdio.h> int fibo(int n) { if (n==1) return 1; if (n==2) return 1; return fibo(n-1) + fibo(n-2); } int main() { int i; printf("Enter n = "); scanf("%d", &i); printf("%d\n", fibo(i)); return 0; }an= ⎛
⎝1 2(1+√5) ⎞
⎠n
− ⎛
⎝1 2(1−√5) ⎞
⎠n
√5. - Alternative to 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + …+ n.
The following program computes
1+2+3+ …+ n. #include <stdio.h> int mysum(int n) { if (n==0) return 0; return n + mysum(n-1); } int main() { int n; printf("Enter n = "); scanf("%d", &n); printf("1+2+....+%d =%d \n", n, mysum(n)); return 0; } - Another example of recursive algorithm:
If a sequence of numbers is generated by the following rules, what is
a20 ?
an = 4an−1 − 6 an−2, a1 = 1, a2 = 3. (1) #include <stdio.h> int mysequence(int n) { if (n==1) return 1; if (n==2) return 3; return 4*mysequence(n-1)-6*mysequence(n-2); } int main() { int n; printf("Enter n = "); scanf("%d", &n); printf("%d\n",mysequence(n)); return 0; }

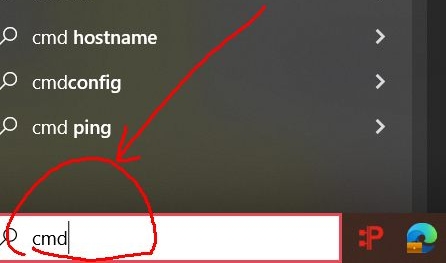 cd to c:\gcc-2.95.2 and run
mingw32.bat to add the path. If you want to run gcc from
any folder, add the folder
c:\gcc-2.95.2
to the PATH environmental variable (details in class).
cd to c:\gcc-2.95.2 and run
mingw32.bat to add the path. If you want to run gcc from
any folder, add the folder
c:\gcc-2.95.2
to the PATH environmental variable (details in class).